Mashhad alluvial aquifer system is the primary water supply for drinking water, irrigation, animal production, and industry in the region. Expansion of irrigated agriculture throughout the past 50 years has helped make the Mashhad plain one of the most productive agricultural regions in Khorasan Razavi province. Extensive withdrawals of groundwater for irrigation have caused water-level declines in many parts of the aquifer and increased concerns about the long-term sustainability of the aquifer.
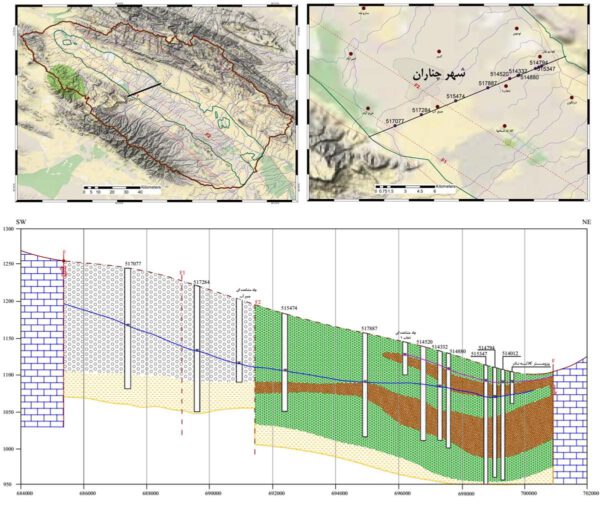
This study assesses groundwater resources in the complex Mashhad alluvial aquifer system. A conceptual model of the Mashhad alluvial aquifer system was developed for a regional assessment of groundwater availability as part of a national water census.
Quantification of water-budget components is a prerequisite for effective water-resources management. Water-budget components analyzed as part of this study were actual evapotranspiration, recharge, surface runoff, groundwater fluxes to and from adjacent geologic units, and groundwater in storage. These components were assessed for 2009 through 2018.